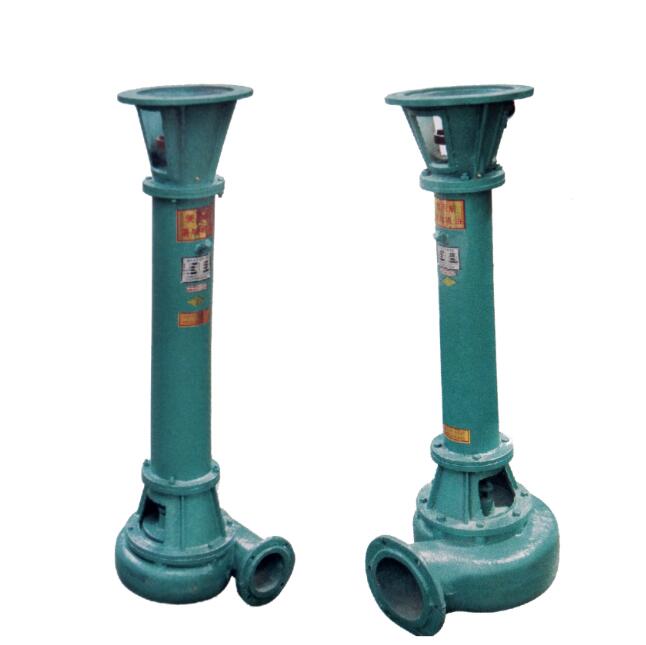
The definition of pump: the pump is controlled by the prime mover, drives the medium movement, it is the energy conversion device which converts the energy into the pressure energy of the medium.
Use of pumps: pumps are mainly used to transport liquid, including water, oil, acid and alkali liquid, emulsion, suspension emulsion and liquid metal, etc., can also transport liquid, gas mixture and liquid containing suspended solids.
Pump performance parameters: the main flow and head, in addition to the shaft power, speed and the necessary cavitation margin. Flow is defined in unit time through the pump outlet output quantity of the liquid, the general use of the volume flow rate; the head is unit of weight in the transportation of liquid from the energy increment of pump inlet to the outlet, for positive displacement pumps, energy increment is mainly reflected in the pressure will increase, it is usually to pressure increase quantity instead of the lift to said. Pump efficiency is not an independent performance parameters, it can be other performance parameters such as flow, head and shaft power calculated by the formula. On the contrary, the known flow, head and efficiency, but also for the shaft power. Between the various performance parameters of the pump there are certain interdependent relationship between can through the test of the pump, respectively, measured and calculated parameter values, and draw into a curve that, these curves called characteristic curve of the pump. Each pump has a specific characteristic curve, which is provided by the pump manufacturer. Commonly used in the plant is also indicated on the characteristics of the curve is recommended to use the performance section, known as the scope of the pump.
The actual working point of the pump is determined by the curve of the pump and the intersection of the characteristic curve of the pump. Selection and use of the pump, the pump should be left to work within the scope of work to ensure that the operation of the economy and safety. In addition, the same pump conveying viscosity of different liquids, the characteristics of the curve will be changed. Usually, the characteristic curve of pump manufacturing plant is mainly refers to the characteristic curve of conveying clean cold water. For the power pump, with the liquid viscosity increases, head and efficiency is reduced, the shaft power is increased, so sometimes the viscosity of the liquid is heated to make the viscosity smaller, in order to improve the transmission efficiency.
Performance range from the pump, giant pump flow up to hundreds of thousands of cubic meters per hour, and the flow rate of the micropump per hour is below a few ml; pump pressure can from atmospheric pressure up to 19.61Mpa (200kgf / cm2) above; be transported liquid temperature minimum up to 200 DEG C, up to a maximum of 800 DEG C or higher. There are many kinds of pumps, such as transportation of water (water, sewage, etc.), oil, acid and alkali, suspension, and liquid metals.